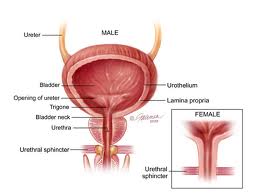
Bladder
The urinary bladder is the organ that collects urine excreted by the kidneys before disposal by urination (micturition). The bladder is a hollow, muscular, and distensible (elastic) organ that sits on the muscles of the pelvic floor. Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra.
The urinary bladder usually holds 300-400 ml of urine. As urine accumulates, the wall of the bladder thins as it stretches, allowing the bladder to store larger amounts of urine without a significant rise in pressure.
Frequent urination can be due to excessive urine production, small bladder capacity, irritability or incomplete emptying. Males with an enlarged prostate urinate more frequently.
Conditions treated
Treatments & Procedures
Bladder cancer
- Flexible cystoscopy
- TURBT (transurethral resection of bladder cancer)
- Cystectomy (removal of the bladder)
Overactive bladder
- urodynamics
- medical treatment of symptoms
- botulinum toxin into the bladder
Urinary tract infections
- cystoscopy
- medical treatment