Urinary Stone Disease
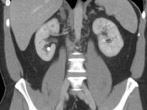
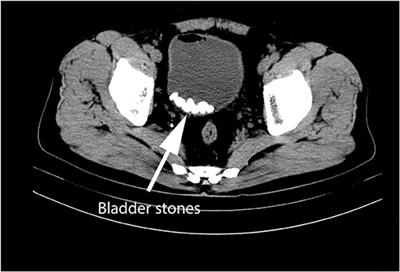
Urinary stones may present anywhere in the urinary tract. Up to 10% of the UK population will present with a stone in their lifetime. Some patients form stones regularly. For more detailed information about stones and the research in Oxford into the causes and treatment of kidney stones please see the Oxford Stone Group website
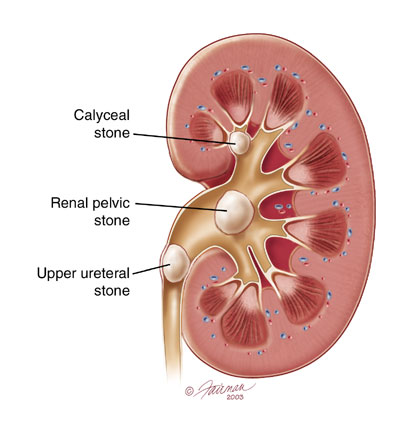
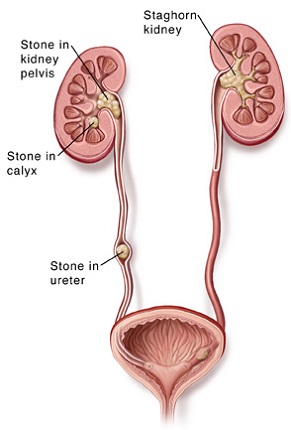
Kidney stones
Around 8% of adult patients have an asymptomatic stone in their kidney. These stones may grow or migrate into the ureter (drainage tube from kidney to bladder) and cause extreme pain.
Ureteric stones
Stones that form in the kidney may migrate into the ureter. Even stones measuring 2 or 3mm in diameter may cause extreme pain. Women who have experienced childbirth and kidney stones say that kidney stone pain is more extreme!